What is Inflation? – Definition, Causes, Examples
Last Updated :
22 Sep, 2023
Have you ever thought that what you used to buy in some rupees earlier, over time you pay more money for the same thing? For example, earlier you used to buy 1 packet of biscuits for 20 rupees now you pay 25 rupees for the same. But why the price of this biscuit has increased, the quality seems to be the same and if you understand this in another way, What happened to the money that earlier it can buy biscuits for 20 but now it will be able to buy the same biscuit for 25. So to know the reason for this, we have to understand inflation.
Inflation is the prices of goods increased in the economy or how much expensive commodities have become over a certain period. It is a familiar word in economics. This inflation has put many countries in the instability stage. In 1974 United States President declared Inflation a Public Enemy.
What is Inflation?
It is a broad measure, of the rate of increase in price over a given period. But this can be narrowed down to some particular sectors such as service sectors, and energy sectors. It allows a representation of a good’s price in the economy. With the increasing inflation the purchasing power impacts which ultimately leads to the decline of economic growth. Unchecked inflation can topple the economy of the country.
There are different conditions of Inflation such as:
- Creeping Inflation: Which is slow rate inflation in which the inflation rate varies from 2 to 3%. Economists thought that this inflation is good for the economy as customers buy now to avoid higher future prices.
- Walking Inflation: This type of inflation is harmful as it ranges from 3 to 10% because people start purchasing more than the actual need resulting in higher demand which cannot be fulfilled by current supplies.
- Galloping Inflation: This type of inflation eats the economy. Money losses its value so quickly that common people’s salaries could not match the price of the commodities. The value is more than 10% in this type.
- Hyperinflation: When the inflation is more than 50% even a bundle of currency would be unable to buy the needed commodities. This type of inflation happens during wartime.
- Core Inflation: It is the rate of measure in the price of everything, except the food because the food is indirectly connected with this type of inflation. When the gas price increases the cost of transportation of food increases also anything related to gas increases.
- Stagflation: In this case, the country’s economic growth goes down but inflation goes up. The reason for stagflation can be when a country undergoing a recession but the country’s import cost increases, hence inflation would also increase.
Cause of Inflation:
All the causes of inflation are due to the gap in demand and supply of commodities.
Types-
- Cost-Push Effect: When the cost of production of commodities increases such as labor wages, and raw materials. Which is transferred to consumers by making higher prices of commodities.
- Demand-Pull Inflation: This happens when the supply of the commodities could not match the demand in the market. This could be understood by, when you want to buy a cricket match ticket from a dealer there were 3 tickets but if the number of customers is 7 then the dealer will increase the price of the ticket to get more profit.
- Built-in Inflation: This type of inflation occurs when the workforce starts demanding higher wages which leads to businesses raising the prices of their goods/services in order to keep up with their cost and expenses. This scenario leads to built-in inflation.
Causes-
- Money Supply: This increased money supply will increase the purchasing power of the customer then they will bid for a few commodities in large amounts, which leads to demand-pull inflation. Even some governments used to print more money to get more votes from the public but this ultimately hampers the economy of the country.
- Policies and Regulations: Giving free commodities to the public will increase in demand for that commodity. Giving people something for free, then the price of that particular thing will become 0, but to get the production cost of this free thing, the government will make other things expensive.
- Wages Inflation: When the money in the hand of the people would increase resulting in their purchasing power increasing hence there could be a shortage of commodities due to more purchasers. Also when unemployment is low there is a low chance of replacing the employers thus increasing their wages and leading to wage inflation.
What if Inflation is ZERO?
We put before you another interesting question, What will happen if the inflation of a country becomes 0? You will think that now things will not be expensive, now you will get things cheap, you will be able to save more, then all this will be a very good thing.
But if we look deeper, and if we see all the reasons for inflation, keeping them in mind, then we will understand that zero inflation is not right. Its effect will be that now companies will increase our salary. And if it is thought that if there are deflations, then every year the price of things will keep going down. People will start reducing expenses and saving more, this will damage the business and people will lose their jobs.
Inflation vs Unemployment
There is a very interesting relationship between unemployment and inflation. This relation is explained through Philips Curve.
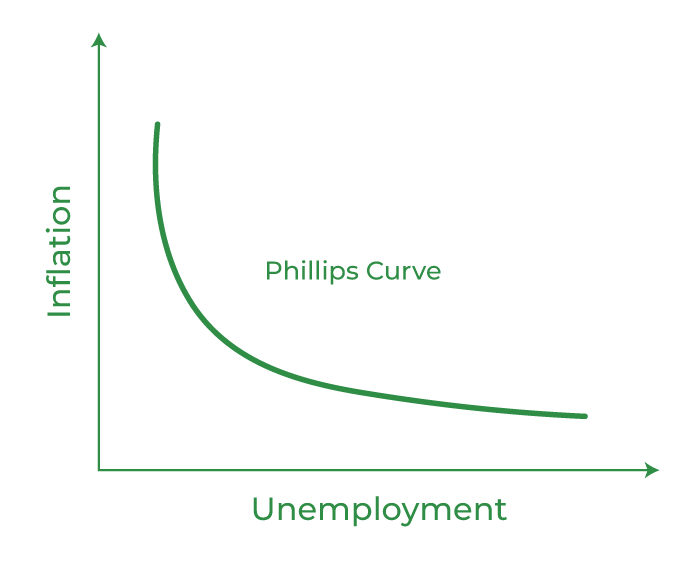
This curve shows that unemployment and inflation are inversely proportional to each other. This means if Inflation goes up unemployment rate will go down and vice versa. But there is some limitation to this curve which means this curve is not valid in case of hyperinflation also there are some political factors that may cause inflation to rise. But normally, this graph is valid.
Lastly, we have understood that inflation will directly affect common people. To avoid the inflation effect people invest money in different assets by taking a risk. But in the current state, this is the only way one can beat inflation.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...